I. Introduction
1. Application
The STED is used in conjunction with large-scale ethylene units to separate and recover polymer-grade styrene product from pyrolysis gasoline.
2. Process Description
The typical process flow diagram of STED unit is shown in Fig.1. It consists of 4 sections: Pre-fractionation, Phenylacetylene Selective Hydrogenation, Styrene Extractive Distillation, and Decolorization. The hydrocarbon feed is sent to the vacuum distillation column to obtain C8 fraction enriched in styrene and C9+ fraction. After phenylacetylene selective hydrogenation, the C8 fraction is sent to the extractive distillation column. Since the effect of sulfolane solvent on the relative volatility of styrene and C8 aromatics is different, the separation of styrene can be achieved. C8 raffinate is collected at the top of the extractive distillation column while crude styrene is obtained at the top of the recovery column. Finally, the crude styrene is sent to the Decolorization part to produce polymer-grade styrene.
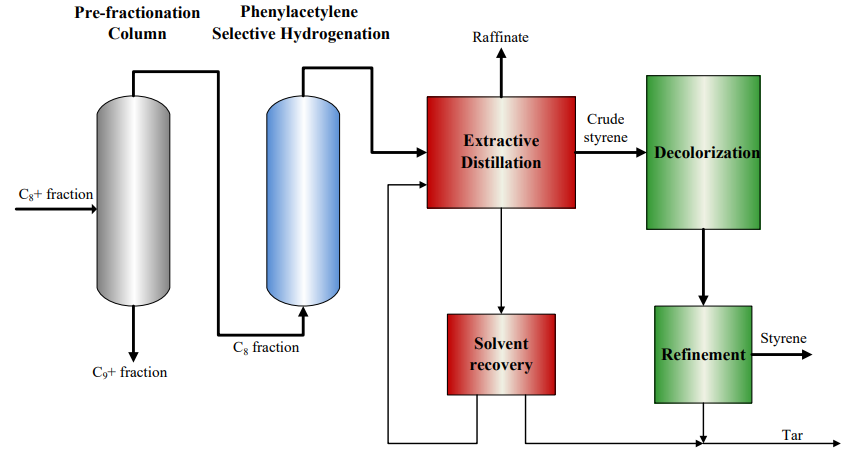
Fig. 1 STED Process flow diagram
3. Main Operating Conditions
Table 1 Main Operating Parameters
| Items | Operating parameters |
| Phenylacetylene Hydrogenation Reaction Temp., ℃ | 25~50 |
| Phenylacetylene Hydrogenation Reaction Pres., MPa(g) | 0.15~0.30 |
| Solvent/Feed Ratio, w | 3.5~5.5 |
| ED Column Top Pres., MPa(g) | -0.08~-0.09 |
| ED Column Top Temp., ℃ | 65~80 |
| Recovery Column Top Pres., MPa(g) | -0.08~-0.09 |
| Recovery Column Bottom Temp., ℃ | 120~140 |
II. Technical Features
1. Feedstock Flexibility
Pyrolysis gasoline from naphtha, diesel, or hydrogenated tail oil as raw material can be treated by STED. There are no special requirements for the feedstock specifications.
2. Product Specifications and Recovery Rate
The STED process uses a highly selective phenylacetylene hydrogenation catalyst, composite solvent, advanced and reliable decolorization technology to ensure high quality and high recovery rate. The product specifications and recovery rate are listed in Tables 2~4.
Table 2 Styrene Specifications
| Items | Specifications |
| Purification, w% | ≥99.9 |
| Ethylbenzene, mg/kg | ≤500 |
| Polymer, mg/kg | ≤10 |
| Peroxide (calculated as H2O2), mg/kg | ≤50 |
| Total aldehyde (based on benzaldehyde), mg/kg | ≤100 |
| Color (Pt-Co) | ≤10 |
| Polymerization inhibitor (TBC), mg/kg | 10~15 |
Table 3 Raffinate Specifications
| Items | Specifications |
| Solvent, mg/kg | ≤1 |
| Styrene, w% | ≤1 |
Table 4 Styrene Recovery Rate
| Items | Index |
| Styrene recovery rate, w% | ≥95 |
3. Long-term Stable Operation
The excellent solvent and polymerization inhibitor as well as the unique solvent regeneration technology used in the STED ensure long-term(≥4 years) stable operation of the unit. The first unit has been in stable operation for more than 10 years since it was put into operation in June 2011.
4. Technical Economy
The typical utility and chemical consumptions of the STED unit are listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Utility and Chemical Consumptions
| Items | Value |
| Cooling water( ⊿t=7℃), t/t f | 70 |
| Low pressure steam, t/t feed | 0.65 |
| Electricity, kWh/t feed | 17 |
| Solvent, g/t feed | <1 |
The total investment is about 160 million RMB for a STED commercial unit with a capacity of 30KMTA installed in China in 2018.
III. Commercial Experiences
By 2021, the technology has licensed 12 units, of which 7 units have been on stream, and the remaining 5 units are in design or under construction. The largest styrene capacity is 40KMTA, and the total capacity of styrene product is 360 KMTA.

Fig. 2 STED unit of Guangdong Xinhuayue with capacity of 30KMTA

