I. Introduction
Inferior diesels has high sulfur, nitrogen, aromatics and olefin content, low cetane number, poor stability, thus it cannot be used profitably. In order to convert these diesels into high-value products, SINOPEC has developed a medium-pressure hydro-upgrading technology (MHUG). This technology is designed to upgrade a variety of diesel feedstocks, including FCC (or MIP and DCC ) LCO, coker gas oil, straight run diesel (AGO) or their blend with straight-run light VGO to produce superior products : naphtha with high potential aromatics used as feedstock for catalytic reforming, low sulfur diesel with high cetane number used as a clean diesel component, and the tail oil (unconverted oil ) with low BMCI used as ethylene-plant feedstock.
II. Process Description
The MHUG process mainly includes reaction and fractionation sections. The mixture of feedstock and hydrogen is heated and fed to a hydrotreating reactor (the first one) where the reactions of HDS, HDN, hydrogenation saturation of olefin and aromatics occur, and then sent to hydrocracking reactor (the second one) where selective ring-opening and cracking reactions occur. Effluent from the second reactor is routed to a separator. After separating out the hydrogen-rich gas stream, the liquid stream is introduced into a fractionator where different products including naphtha, diesel and tail oil can be obtained. If required, the tail oil (unconverted oil) can be partially or fully recycled to the first or second reactor. A simplified process flow diagram for MHUG process is shown below.
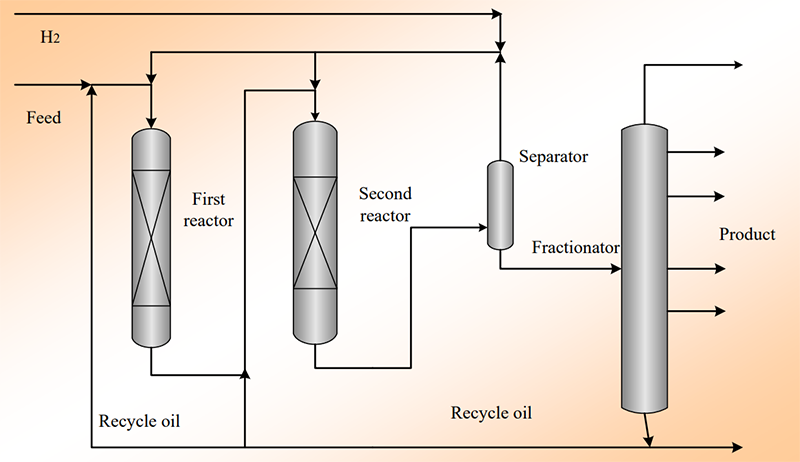
Operating conditions:
Hydrogen partial pressure, MPa: 4.5~12.0
Temperature, °C: 340~400
LHSV, h-1: 0.5~2.0
Reactor inlet H2/oil ratio,Nm3/m3: 400~600
Performance:
In the MHUG process unit, when treating different feedstocks under the typical operating conditions, the heavy naphtha yield is 5%~73% with potential aromatics more than 50%; the diesel yield is 0~95 wt% with the cetane number increase by 10 ~ 20 units and the sulfur content less than 10 wppm.
The operating range of the process unit is 60%~110% of designed capacity.
MHUG technology has many commercial applications, and no special safety and environmental protection problems during production.
III. Main features of the Technology
MHUG is an advanced, mature, reliable and cost-effective technology with relative low operating pressure, low chemical hydrogen consumption, and low energy consumption.
MHUG has feedstock adaptability. This technology can be used to treat LCO, coker gas oil, straight run diesel (AGO), LVGO or blends of them.
The product yields are high, the products are superior in quality.
MHUG has two operating modes with high flexibility, a once-through mode and an unconverted oil recycling mode. Depending on user's demand, the different yield patterns can be selected: maximum catalytic reforming feed yield, maximum diesel yield, or maximum unconverted oil and simultaneously producing jet fuel.
IV. Catalysts
MHUG technology uses a combined catalyst system including guard catalysts, hydrotreating catalysts, hydrocracking catalysts. The hydrotreating catalyst is RN-410、RN-510, the hydrocracking catalyst is RIC-3 and RHC-210, their physical and chemical properties are also listed in Table 1.
Table 1 The properties of the catalysts
| Items | RN-410 | RN-510 | RIC-3 | RHC-210 |
| Function | Hydrotreating | Hydrotreating | Hydrocracking | Hydrocracking |
| Active metal | Ni-Mo | Ni-Mo | Ni-W | Ni-W |
| Shape | Butterfly | Butterfly | Butterfly | Butterfly |
| Pore volume, ml/g | ≮0.25 | ≮0.44 | ≮0.23 | ≮0.2 |
| Specific surface area, m2/g | ≮140 | ≮150 | ≮200 | ≮250 |
| Size, mm | ~1.3/~3.4 | ~1.3/~3.4 | ~1.3 | ~1.3 |
| Crushing strength,N/mm | ≮18 | ≮18 | ≮18 | ≮18 |
V. Commercial Experience
MHUG technology has been used in 25 commercial units, the largest unit among them has a capacity of 3.6 MMTA, and the catalysts have been applied in industrial units for 58 times.

