I. Introduction
1. Technology Background
RMC developed by SINOPEC is a hydrocracking technology under medium pressure. The feedstock of RMC can be VGO or mixture of VGO and CGO or LCO. RMC is developed to produce heavy naphtha with high potential aromatic content, clean diesel with high cetane number and good unconverted oil used as ethylene cracking feed or lubricant base oil feed. The catalysts used for RMC include hydrotreating catalyst with good denitrification and aromatics saturation performance, and hydrocracking catalyst with high selectivity and stability. These two types of catalysts can relieve the decrease of the HDN and HDA reaction rate caused by lower H2 pressure.
RMC II, the second generation of RMC, improves the feedstock adaptability for inferior oil, and reduces the BMCI value of unconverted oil and increases paraffin content of unconverted oil.
Operation flexibility is improved as well.
2. Process Schematic Drawing
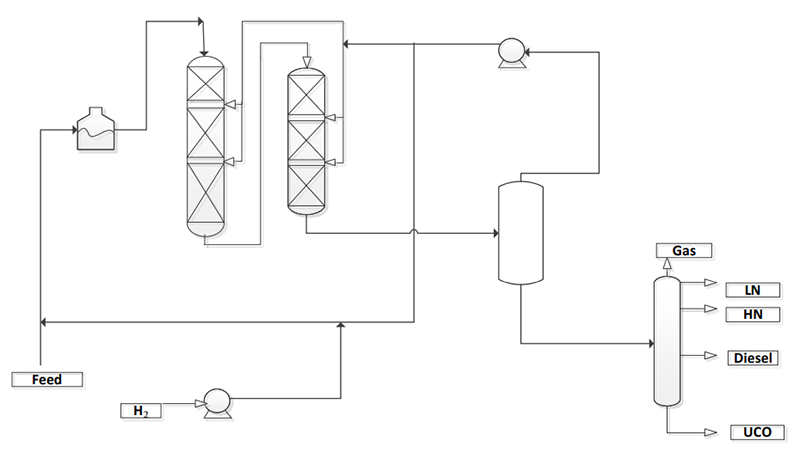
A single stage once-through process is applied for the RMC technology as shown as Figure 1. After heated in the furnace, the heavy feed like VGO mixed with hydrogen is introduced into the first fixed bed reactor, where desulfurization (HDS), denitrification (HDN), and aromatics saturation (HDA) reactions occur. Then the mixture goes into the second reactor where not only HDS, HDN and HDA but also ring-opening, cracking and isomerization reactions occur. The reaction effluents are sent to the separation system to separate the gaseous stream with rich hydrogen which is cycled back to the reactor by the compressor for circulation and then the liquid stream flows to the fractionator to obtain light naphtha, heavy naphtha, jet fuel, diesel and unconverted oil.
LTAG with two operating modes has been successfully commercialized (see Figure). In Mode I, LCO is introduced into a hydrotreating unit, and the hydro-LCO produced returns to the original FCC riser reactor as sole feedstock. For gasoline produced by LTAG Mode I, the content of olefins is less than 10 vol% and the RON may reach to 94. Moreover, light aromatics can be produced, where the yield of C6-C10 alkylbenzene can be more than 35.5%. In Mode II, both heavy oil and hydro-LCO serve as the feedstock of FCC riser. To process hydro-LCO and heavy oil separately in the same FCC riser, an additional conversion zone at the lower section of the riser is introduced. For gasoline produced by LTAG Mode II, the content of olefins can decrease 4.0~ 5.0 units and the RON can increase 0.5~1.0 unit. Both in Mode I and in Mode II, ~70wt% of once-through conversion of hydro-LCO, ~90wt% of LPG and Gasoline selectivity and ~ 2.5wt% of H2 consumption can be achieved. Full conversion of LCO can be achieved by using cyclic operation.
3. Main Operation Parameters
Reaction pressure: 8.0~12.0 MPa (hydrogen partial pressure)
LHSV: 0.5~1.0 h-1
Temperature: 350~415°C
H2/Oil: 800~1200
II. Technical Features
Operation Flexibility
RMC presents good operation flexibility. Different product schemes can be realized by adjusting operating conditions and cutting schemes. According to the refiners' needs, optimized parameters are chosen to obtain the maximum naphtha, maximum kerosene, maximum diesel or maximum unconverted oil.
Feedstock Adaptability
With the presence of the high performance catalysts and at medium pressure, RMC can process the feed similar to high pressure hydrocracking, including VGO or mixture of VGO or CGO and/or LCO.
Product Specifications
The heavy naphtha yield is 10%~40% while processing heavy VGO with high sulfur content and FBP over 520℃ at hydrogen partial pressure of 8.0 ~ 12.0 MPa. The potential aromatic content of 2 the heavy naphtha is over 50%wt, it is good for reforming feedstock. Also 25%~50% diesel can be obtained, diesel product meets Euro V emission standard. The unconverted oil yield is 25%~60%, with BMCI value of 8~12, good to be used as ethylene cracking feed or lubricant base oil feed.
Operation Cycle
The operation cycle is not less than 4 years, and the lifetime of the main catalysts is not less than 8 years.
III. Catalyst
There are two kinds of main catalysts used for RMC. One is hydrotreating catalyst and the other is hydrocracking catalyst. Hydrotreating catalysts include RN-32V and RN-410, and hydrocracking catalysts include RHC-220, RHC-133 and RHC-131. Table 1 shows properties of the typical catalysts.
Table 1 Properties of the Typical Catalysts for RMC
| Grade | RN-32V | RN-410 | RHC-220 | RHC-133 | RHC-131 |
| Type | Hydrofining | Hydrofining | Hydrocracking | Hydrocracking | Hydrocracking |
| Metal Components | Ni-Mo-W | Ni-Mo | Ni-W | Ni-W | Ni-W |
| BET, m2/g | ≮150 | ≮140 | ≮200 | ≮165 | ≮165 |
| Pore Volume, ml/g | ≮0.24 | ≮0.25 | ≮0.20 | ≮0.27 | ≮0.27 |
| Crushing Strength (N/mm) | ≮18 | ≮18 | ≮18 | ≮18 | ≮18 |
| Appearance | Butterfly | Butterfly | Butterfly | Butterfly | Butterfly |
IV. Industrial Applications
7 industrial applications have been realized, and the largest capacity of the units is 1.5MMTA.

